A kidney transplant is a transplantation procedure whereby a functioning kidney from either an alive or recently deceased donor substitutes a kidney that is badly damaged or malfunctioning.

For people with end-stage kidney diseases, this intervention is praised as a life-preserving treatment that gives them the chance to improve the quality of their lives and preserve their kidney functions.
A kidney transplant is a difficult but incredibly effective therapeutic option for those with end-stage kidney diseases, offering a new perspective and improved wellbeing.
The thorough assessment of the patient, the diligent post-operative care, and the uncompromising commitment to medical advice all play a critical role in the effectiveness and durability of the donated kidney.
About Kidney Transplant

Symptoms:
Here are some common symptoms associated with kidney transplant:
Surgical Recovery Symptoms:
- Pain and discomfort at the surgical site
- Swelling or bruising around the incision area
- Limited mobility and range of motion initially
- Fatigue and weakness during the recovery period
General Symptoms:
- Fever or chills
- Unexplained weight loss
- Persistent nausea or vomiting
- Shortness of breath
- Skin rash or itching
Immunosuppressive Medication Symptoms:
- Increased susceptibility to infections
- Flu-like symptoms (fever, body aches)
- Gastrointestinal disturbances (nausea, diarrhea)
- Elevated blood pressure
- Changes in blood sugar levels
Rejection-related Symptoms:
- Decreased urine output
- Elevated blood pressure
- Swelling
- Weight gain
- Elevated levels of creatinine or BUN (blood urea nitrogen)
Complication-related Symptoms:
- Pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen or back
- Difficulty urinating or changes in urine colour or appearance
- Signs of infection at the surgical site (redness, warmth, pus)
- Signs of organ rejection, such as fever, tenderness over the transplant area, and elevated blood pressure
Medication-related Symptoms:
- Nausea or vomiting due to medications
- Increased hair growth
- Osteoporosis-related symptoms (bone pain, fractures)
- Skin changes (acne, thinning skin)
- Mood changes or sleep disturbances
Post-Transplant Care Symptoms:
- Elevated blood pressure or changes in blood pressure medication requirements
- Changes in weight or fluid retention
- Graft dysfunction, indicated by rising creatinine levels
Have a look at : Panchakarma Treatment
Types:

There are two main types of kidney transplants:
- Living Donor Kidney Transplant: Living donor kidney transplants involve a healthy kidney donated by a living person, offering advantages like shorter waiting times, improved organ quality, and potentially improved outcomes. The two main categories within living donor kidney transplants are:
- Related Donor Transplant
- Non-Related Donor Transplant
- Deceased Donor Kidney Transplant: In this kind of transplant, the deceased person’s (cadaveric donor) kidney is obtained after they freely donated their organs via a legal agreement or a consented organ donation program.
Based on compatibility and organ availability, waiting lists for deceased donor kidney transplants exist. Kidney transplants from dead donors fall into two primary categories:
- Standard Criteria Donor (SCD) Transplant
- Expanded Criteria Donor (ECD) Transplant
Read about – Angioplasty
Treatment of Kidney Transplant
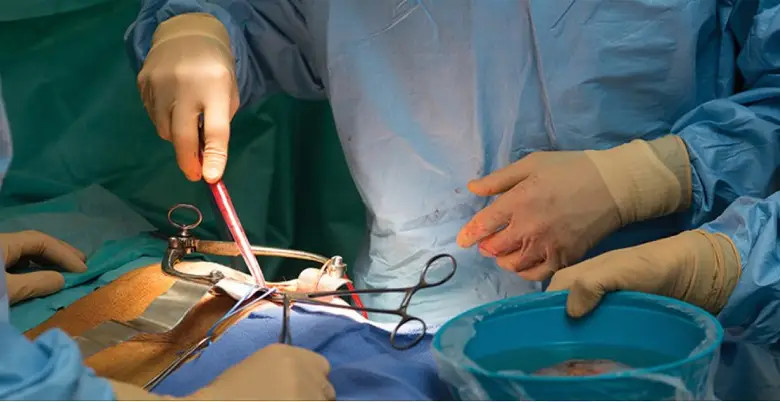
- Prognosis: The prognosis post-transplant is generally positive, with many patients experiencing improved kidney function and reduced reliance on dialysis.
- Risk Factors: Risk factors for transplant rejection include non-compliance with medications, infection, and pre-existing health conditions.
- Side Effects: Immunosuppressive medications, necessary to prevent rejection, can lead to side effects like increased susceptibility to infections, bone thinning, and high blood pressure.
- Pre / Post Care: Pre-transplant care includes medical assessments, managing comorbidities, and ensuring the patient is physically fit for surgery. Post-transplant care involves close monitoring, adherence to medications, and regular follow-up appointments.
Explore more about – Liver cancer
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis involves blood tests, imaging (ultrasound, CT scan), and a thorough medical evaluation to assess the patient’s overall health and suitability for transplantation.
Outlook:

The outlook after a kidney transplant surgery can vary depending on several factors, including the recipient’s overall health, the quality of the donor organ, and how well the body accepts the new kidney. Here are some key points to consider regarding the outlook after kidney transplant surgery:
Read about – Heart Blockage Treatment
- Immediate Recovery
- Immunosuppressive Medications
- Kidney Function
- Rejection and Complications
- Lifestyle Changes
- Follow-Up Care
- Psychological Adjustment
Treatment Cost of Kidney Transplant
A kidney transplant in India typically costs between 5 and 20 lakh rupees, depending on the type of donor, the hospital, the location, the level of experience on the medical staff, and any potential complications.

- Pre-operative Evaluations: These tests, which can cost anywhere between 20,000 and 50,000 rupees, are performed on the patient to assess their health and fitness for transplantation.
- Surgical Procedure: Surgical costs range from 3 lakh to 8 lakh rupees or more and cover the transplant procedure, surgical team costs, anaesthesia, and operating room costs.
- Hospital Stay: The cost of post-operative hospitalization, which includes lodging and board, nursing care, and medical supplies, can range from 1 lakh to 2 lakh rupees or more.
- Medicines: Immunosuppressive drugs can be expensive, costing between 10,000 and 20,000 rupees each month, but they are necessary to prevent organ rejection.
- Follow-up Care: Post-transplant follow-up checkups, testing, and consultations might cost several thousand rupees over time but are essential for the success of the treatment.