Surgery to replace a failing or a damaged heart with a healthy heart from a person who donated it is known as a heart transplant. People with severe heart problems who are unresponsive to other medical therapies frequently contemplate this operation.
A transplanted heart can greatly raise a patient’s probability of survival while enhancing their quality of life.
About Heart Transplant
Cardiovascular illness, usually referred to as heart disease, is a broad term for several ailments that have an impact on the circulatory system and coronary arteries.
It may result in cardiac failure, wherein the heart’s capacity to pump blood is impaired and a heart transplant is required.
You Should also know – Immunotherapy
Symptoms:
When a person’s heart condition has gotten so bad that existing medical therapies are ineffective at controlling their symptoms and enhancing their quality of life, they may need a heart transplant.
Severe signs of progressive heart failure are frequently present in those who need a heart transplant. These signs may appear as:
- Severe Shortness of Breath
- Chronic Fatigue
- Persistent Chest Pain
- Fluid Retention and Swelling
- Rapid or Irregular Heartbeat
- Inability to Perform Daily Activities
- Frequent Dizziness or Light-headedness
- Coughing and Wheezing
- Unintended Weight Loss
- Worsening of Existing Heart Conditions
- Reduced Appetite
Have you looked at : Kidney Transplant
Types:
Heart transplants often fall into one of two categories: orthotopic heart transplant or heterotopic heart transplant. The position of the transplanted heart within the recipient’s body varies between these types.
- Orthotopic Heart Transplant: To ensure normal blood flow into and out of the transplanted heart, an orthotopic heart transplant includes removing the recipient’s failing heart and replacing it with a healthy donor heart in the same anatomic position.
- Heterotopic Heart Transplant: When the recipient’s heart is too weak to function on its own, heterotopic heart transplants include placing the donor heart next to the failing heart to provide additional support.
Read about – Panchakarma Treatment
Outlook:
Heart transplantation offers a chance for a longer and healthier life.
However, it’s a complex procedure with considerations such as donor availability, compatibility, and post-transplant care.
Treatment of Heart Transplant
A heart transplant is a major surgical procedure, and while it can be life-saving, it’s not without its challenges.
Complications:
Although heart transplants are difficult operations with several risks, technological advances have improved results.
The management of these problems to guarantee patient safety is a skill that medical teams have. Here are some potential issues that could arise during heart transplantation therapy:
- Organ Rejection
- Infection
- Graft Dysfunction
- Coronary Allograft Vasculopathy
- Side Effects of Medications
- Post-Pericardiotomy Syndrome
- Fluid Accumulation
- Blood Clots
- Bleeding
- Diabetes
- Psychological Challenges
- Chronic Kidney Disease
- Mental Health Issues
- Drug Interactions
- Recurrent Heart Disease
You can also look at : Proton Therapy
Prognosis:
The individual’s general health, adherence to medical advice, the quality of the donor heart, and the administration of post-transplant care are some of the variables that affect the prognosis after a heart transplant.
- Heart transplants greatly enhance quality of life, reduce symptoms of heart failure, and resume regular activities. Because of higher survival rates, many patients are now able to survive for several years after their treatment.
- Organ rejection, immunosuppressive drugs, elevated risks of infections, certain malignancies, and issues brought on by the body’s immune response are some of the post-transplant difficulties.
- Heart transplant recipients need ongoing medical treatment for the rest of their lives, which includes routine check-ups, lab tests, and imaging to monitor the function of their hearts and look for signs of rejection or problems.
- Recipients are counselled to lead a heart-healthy lifestyle in order to preserve the health of the transplanted heart.
- Emotional and psychological difficulties associated with heart transplantation, such as thankfulness, worry, and transition, can be made easier with assistance from family, friends, and mental health specialists.
- Recipients will go through a period of rehabilitation after the transplant procedure to restore strength and mobility.
Risk Factors:
Heart transplant is a complex surgical procedure that comes with certain risk factors that can impact the success of the transplant and the patient’s overall health.
It’s important to understand these risk factors before undergoing a heart transplant:
- Age
- Overall, Health
- Severity of Heart Disease
- Previous Surgeries or Medical Procedures
- Immunosuppressive Medications
- Organ Rejection
- Infection
- Graft Vasculopathy
- Psychosocial Factors
- Donor-Recipient Compatibility
- Surgical Complications
- Post-Transplant Lifestyle
- Long-Term Outlook
Side Effects:
Here are some common side effects:
- Immunosuppressive Medication Side Effects:
– Increased Infection Risk
– Skin Changes
– Gastrointestinal Issues
– Kidney Issues - Diabetes
- High Blood Pressure
- Weight Gain
- Osteoporosis
- Mood Changes and Mental Health Issues
- Cancer Risk
- Lipid Abnormalities
- Hair Loss
- Graft Rejection and Complications
Note – Liver cancer
Pre / Post Care:
Pre-transplant care involves rigorous evaluation and preparation.
Post-transplant care includes taking medications as prescribed, regular medical check-ups, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Heart Transplant Treatment Cost
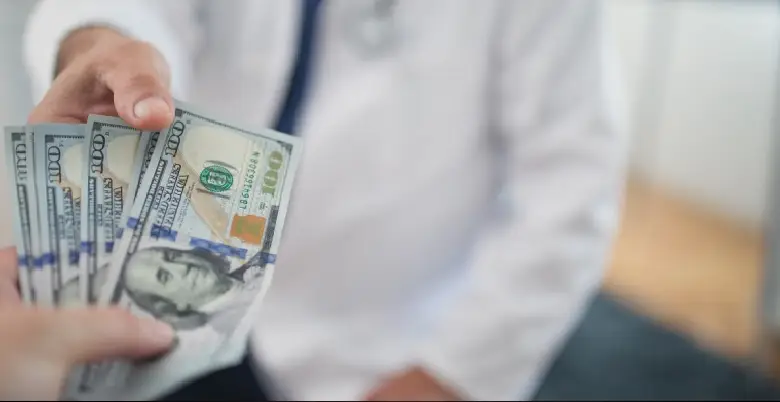

On average, the cost of a heart transplant in India can range from ₹15 lakh to ₹25 lakh or even higher.
It is important to keep in mind that the cost includes various components such as pre-operative evaluations, surgery, post-operative care, hospital stay, medications, follow-up visits, and potential complications.