Modern medical technology has completely changed how we think about cardiovascular health. Numerous lives have been saved and many people’s quality of life has been enhanced thanks to the medical technique known as angioplasty, which has become a mainstay in the treatment of cardiac disorders.
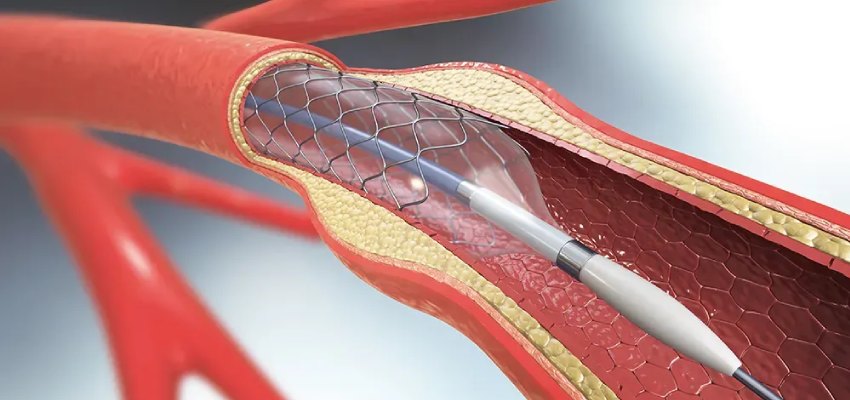
An impressive development in cardiovascular therapy is angioplasty, which provides successful treatment for obstructed or constricted arteries. Angioplasty not only cures symptoms but also enhances patients’ general well-being and lowers the chance of major consequences by restoring blood flow to the heart muscle.
Introduction
Introduction
About Disease
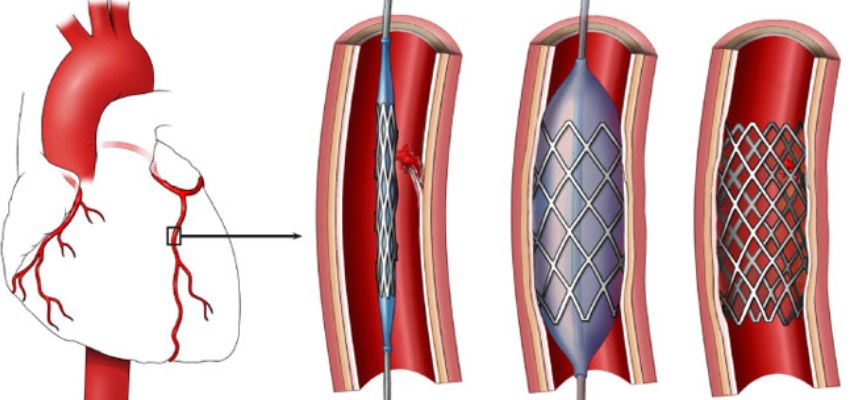
About Angioplasty
Symptoms:
While angioplasty itself is a procedure, there are certain symptoms and indicators that might prompt a doctor to recommend it. Here are some symptoms and conditions that could lead to considering angioplasty:
- Chest Pain (Angina)
- Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction)
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
- Unstable Angina
- Blocked Arteries in Other Parts of the Body
- Angiography Results
Also read about – Liver cancer
Types:
Based on the arteries or blood vessels being treated, several angioplasty methods might be carried out. Here are a few examples of typical types:
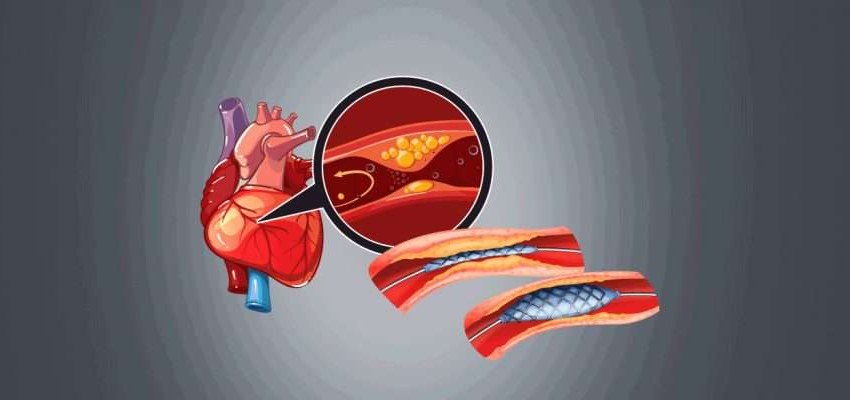
- Coronary Angioplasty (Percutaneous Coronary Intervention – PCI): Angioplasty is a popular technique that uses a catheter with a balloon at its tip to open constrictions or blockages in the coronary arteries. A stent is frequently used in conjunction with angioplasty to keep the coronary arteries open.
- Balloon Angioplasty: Using a balloon to open blocked or restricted arteries, angioplasties can also open peripheral arteries in addition to coronary arteries.
- Coronary Stenting: Coronary angioplasty entails inserting a stent, either bare metal or a drug-eluting stent that releases medication to stop arterial narrowing, to keep the artery open.
- Peripheral Angioplasty: This treatment, which is frequently used to treat peripheral arterial disease (PAD) in the legs and limbs, involves opening blocked or restricted arteries outside the heart.
- Carotid Angioplasty and Stenting: To open blocked or restricted carotid arteries and prevent strokes, carotid angioplasty is a technique that may also involve the implantation of a stent.
- Renal artery angioplasty: It is a treatment for renal artery stenosis, which narrows kidney arteries and improves blood flow while controlling diseases like high blood pressure.
- Venous Angioplasty: This kind of angioplasty is frequently performed to treat clogged or narrowed veins, frequently taking care of diseases like deep vein thrombosis or venous insufficiency.
- Aortic Angioplasty: Aortic angioplasty, which is frequently combined with balloon valvuloplasty or the implantation of an aortic stent, is a treatment used to treat aortic stenosis, which develops when the aortic valve narrows.
- Aneurysm Repair: To treat aneurysms, which are weak spots in an artery that may bulge and rupture, angioplasty is occasionally performed in conjunction with the insertion of stents.
- Subclavian Angioplasty: The subclavian arteries, which are found below the collarbone, are treated with this type of angioplasty when they are obstructed or constricted.
You may also like to read about – Eye Transplant
Treatment
Treatment of Angioplasty
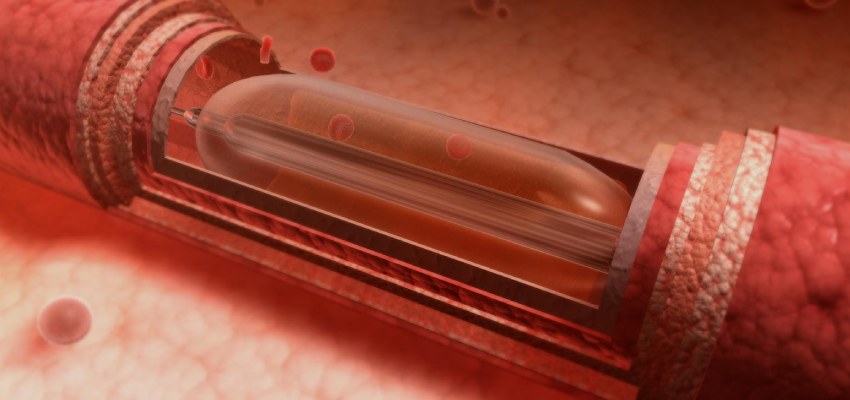

Treatment for various medical conditions can involve a range of approaches, and angioplasty is one of the treatments used to address certain cardiovascular issues.
Let’s explore the treatment landscape, including when angioplasty is used and other potential treatments:
- Angioplasty:
- Coronary Angioplasty (Percutaneous Coronary Intervention – PCI)
- Medications:
- Antiplatelet Drugs
- Cholesterol-Lowering Medications
- Beta-Blockers
- ACE Inhibitors or ARBs
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Healthy Diet
- Regular Exercise
- Smoking Cessation
- Stress Management
- Medication Interventions:
- Thrombolytic Therapy
- Medication for Blood Pressure and Diabetes
- Surgery:
- Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery (CABG)
- Implantable Devices:
- Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD)
- Cardiac Pacemaker
Read about – Heart Blockage Treatment Without Surgery
Diagnosis:
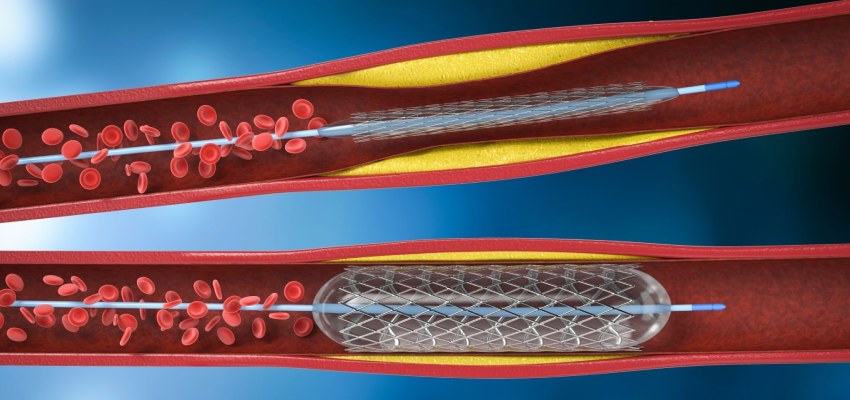
The diagnosis for the need of angioplasty typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, imaging tests, and other diagnostic procedures. Here’s an overview of the diagnosis process:
- Medical History
- Physical Examination
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)
- Stress Tests
- Blood Tests
- Echocardiogram
- Cardiac Catheterization
- CT Angiography
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA)
- Radionuclide Imaging
You should also know – Skin Whitening Treatment
Outlook:
It’s essential to work closely with your healthcare provider to create a personalized care plan and to follow their guidance for medication, lifestyle changes, and follow-up appointments.
By actively participating in your heart health management, you can improve your chances of a positive outlook and enjoy a better quality of life after angioplasty.
Treatment Cost
Angioplasty Treatment Cost

As of my last update in September 2021, here’s a rough estimate of the cost of angioplasty in India:
Coronary Angioplasty (PCI):
- The cost for a basic angioplasty procedure in India can range from around ₹1,00,000 to ₹3,00,000 or more.
- If a drug-eluting stent is used during the angioplasty, the cost can increase significantly. The cost of drug-eluting stents can range from ₹20,000 to ₹1,50,000 or more, depending on the brand and type of stent.