In a complicated surgical intervention known as a liver transplant, a better and healthier liver from a donor is substituted for a diseased or injured liver.
When no other medical or surgical treatments are sufficiently able to restore liver health, it is regarded as the last resort treatment option for people with end-stage liver disease and otherwise acute liver failure.
A major surgical procedure like a liver transplant has risks like organ rejection, disease, bleeding, and issues with immunosuppressive medication. For those who qualify, it does provide a longer and better quality of life.
A multidisciplinary team of specialists works on the liver transplant as a life-saving procedure with the goal of giving patients with irreparable liver damage a healthier, more productive future.
Explore more about – Mole Removal Surgery
Introduction
Liver Transplant Introduction
About Disease
About Liver Transplant
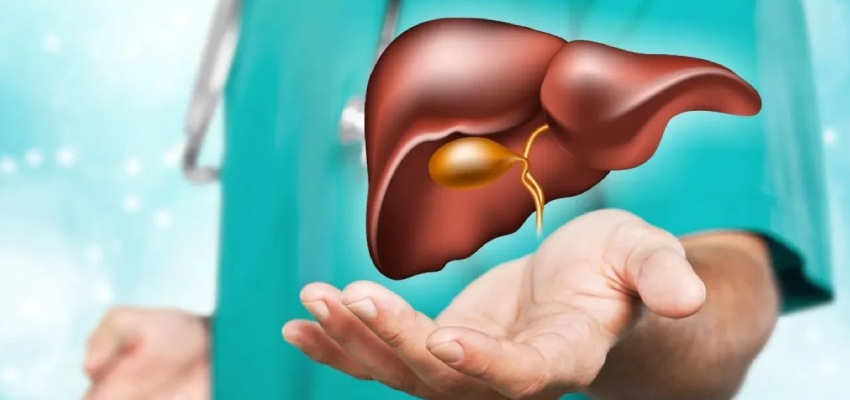
The term “liver disease” refers to a broad range of conditions that can impair the liver’s normal operation.
One of the main reasons for liver transplants is chronic liver disease, which includes cirrhosis, alcoholic liver disease, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and chronic hepatitis B or C.
These conditions cause the liver to gradually deteriorate, scar, and fibrose, which makes the liver less effective at carrying out its essential functions.
Contrarily, acute liver failure is a severe but uncommon condition characterised by a short-term, rapid decline in liver function.
It can be brought on by drug toxicity (such as an overdose of acetaminophen), autoimmune disorders, metabolic diseases, as well as viral infections (such as hepatitis A, B, or E).
Without prompt treatment, acute liver failure can result in complications that are fatal and may require an urgent liver transplant.
A patient’s condition, the severity of their liver disease, and their eligibility for a liver transplant are all assessed by a healthcare staff.
Candidates are put on a waiting list for a liver from a deceased donor or, if a living donor is available, they can investigate that option.
The goal of liver transplant surgery is to replace a diseased liver with a healthy donor liver, which will then regenerate and enlarge to its regular size for both the recipient and the donor.
Following organ transplantation, patients must take lifelong immunosuppressive drugs to prevent organ rejection; this necessitates close monitoring, medical management, and changes in lifestyle for success as well as reducing difficulties.
Patients with acute liver failure and end-stage liver disease now have a much higher chance of survival and a higher quality of life thanks to liver transplants.
Advancements in medical technology and expertise have made liver transplant safe and successful. However, limited donor organ availability necessitates organ donation and awareness about liver disease and transplantation to save more lives.
Have a look at Chemotherapy.
Treatment
Treatment of Liver Transplant
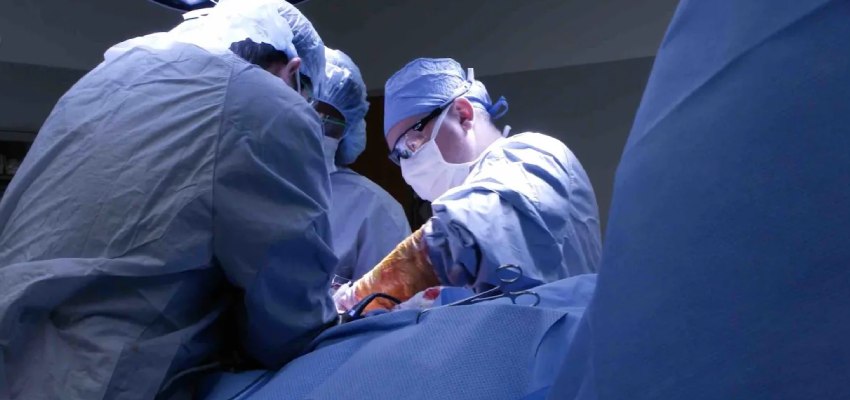
Liver transplant is primarily performed for the following conditions:
- End-Stage Liver Disease: End-stage liver disease is characterized by severe liver damage, rendering it incapable of carrying out crucial tasks like protein synthesis, digestion, and filtration.
Chronic infections, alcohol problem and non-alcoholic liver diseases, liver disease, and autoimmune disorders are among the most typical causes.
- Acute Liver Failure: Acute liver failure is a rapid and unexpected loss of liver function, frequently brought on by drug toxicity, metabolic diseases, or bacterial diseases (such as hepatitis A, B, or E).
Acute liver failure can be fatal if it is not treated quickly.
End-stage liver disease or acute liver failure can be treated with a liver transplant, which involves swapping out the damaged liver for a healthy one from a living or deceased donor.
A talented surgical team is required for this complicated procedure.
Also read about – Knee Replacement Surgery
Treatment Method
- Pre-Transplant Evaluation: Before receiving a transplant, patients go through a thorough assessment to determine their health and suitability for surgery.
This evaluation includes blood tests, imaging studies, and a review of their medical history.
- Donor Selection: Choosing a suitable donor for a living donor liver transplant requires finding that person, usually a family member or relative, and having their liver thoroughly examined to make sure it is healthy and compatible with the recipient.
- Transplant Surgery: Both donors and recipients are brought into the operating room on the day of the transplant.
While deceased donor transplants use the entire donor liver, living donor transplants only use a portion of the donor’s liver.
To ensure proper blood flow and liver function, the surgical team joins blood vessels and bile ducts.
- Post-Transplant Care: The patient is carefully watched in the intensive care unit (ICU) after surgery to avert complications and guarantee the transplanted liver is operating normally.
To stop the recipient’s immune system from rejecting the new liver, immunosuppressive medications are given
Long-Term Follow-Up: Post-transplant care is essential for the success of the procedure and calls for routine follow-up visits to check on the patient’s liver and to review and adjust any medication.
You can also look at Plastic Surgery.
Complications and Risks
Risks associated with liver transplant surgery include organ rejection, infections, haemorrhaging, and bile duct issues.
Medication that suppresses the immune system makes a person more vulnerable to infections and metabolic problems.
Rates of success
Thanks to advancements in surgical methods and immunosuppressive medications, liver transplant success rates have significantly increased over time.
Liver transplant patients typically have high one-year survival rates, and many go on to lead regular, healthy lives.
Do read about Bone Marrow Transplant for your reference.
Treatment Cost
Liver Transplant Treatment Cost in India
Many patients from all over the world choose to have liver transplants in India because of the country’s relatively lower treatment costs when compared to other nations. India is known for offering affordable medical treatments.
When choosing a course of treatment, it is crucial to consider the standard of medical care, the surgical team’s experience, and the hospital’s success rates, as the success of a liver transplant greatly depends on the knowledge and skills of the medical team.
The cost of treating liver transplant disease in India varies depending on several variables, including the hospital, the type of transplant (from a living or deceased donor), the patient’s health, and the length of time post-operative care is needed.
In India, the average cost of a liver transplant can be between 20 lakh and 35 lakh INR.
It is important to understand that this cost is only an estimate and may change.
Pre-transplant evaluation, donor workup (in living donor transplants), immunosuppressive medications, post-operative care, as well as follow-up consultations may all incur additional costs.
The transplant centre and medical staff should be consulted regarding these costs to obtain a more precise estimate of the overall cost.
Read about – Root Canal Treatment
2 comments
Thanks for breaking it down so clearly. I had no idea about liver transplants.
Great info on treatment costs in India.