White blood cells called lymphocytes are the main target of the blood malignancy known as acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
In order to effectively treat ALL, a combination of chemotherapy, targeted therapy, radiation therapy, stem cell transplant, and supportive care is frequently used.
Introduction of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Treatment
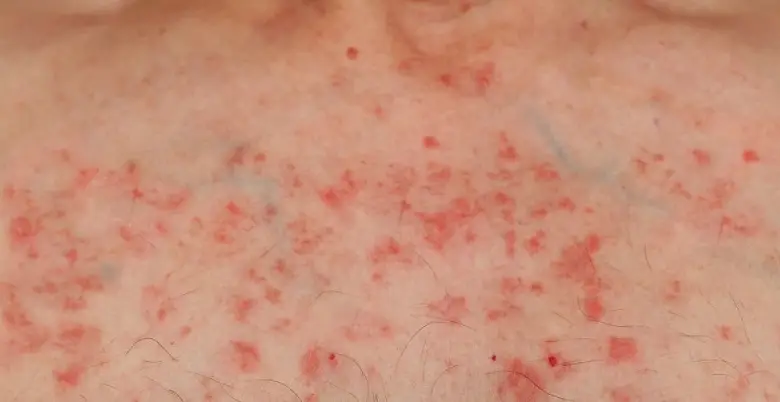
Symptoms
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) is a type of blood cancer that requires prompt medical attention and treatment when suspected. If you or someone you know experiences the following symptoms, it is important to seek medical care promptly:
- Fatigue
- Pale Skin
- Frequent Infections
- Easy Bruising
- Fever
- Bone Pain
- Enlarged Lymph Nodes
- Abdominal Discomfort
- Weight Loss
- Loss of Appetite
- Headaches
- Vomiting
- Breathing Problems
Read about – Acromegaly Treatment
Types
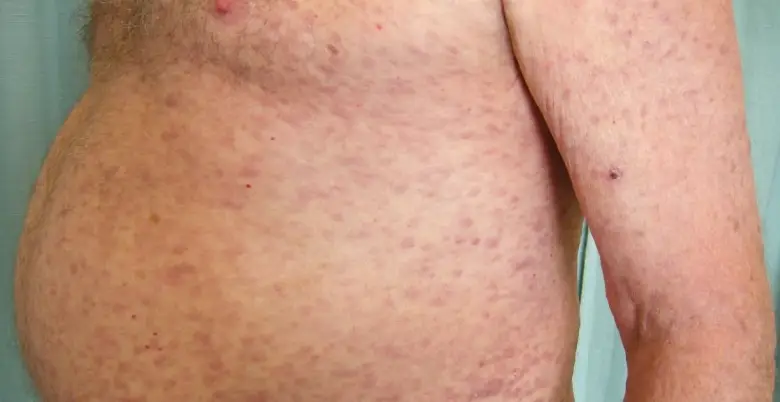
Depending on the state and subtype of ALL of each patient, a combination of medications is frequently used to treat acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). The most common forms of ALL treatment are as follows:
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is the major treatment for ALL and involves the use of potent medications to either destroy or stop the growth and division of cancer cells. Combination regimens and phases such as induction, consolidation, and maintenance therapy are frequently used.
Targeted Therapy: Drugs used in targeted therapy, such as rituximab and inotuzumab ozogamicin, specifically target chemicals or proteins found on the surface of cancer cells, either destroying them or making the immune system more effective at doing so.
Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy targets and destroys cancer cells using high-energy X-rays or other types of radiation.
Stem cell transplant: Also referred to as a bone marrow transplant, this surgery involves replacing the damaged bone marrow of the patient with healthy stem cells from a donor.
Corticosteroids: To reduce inflammation and stop the immune system from attacking cancer cells, corticosteroids like prednisone or dexamethasone are frequently used in ALL treatment.
Intrathecal Therapy: Because ALL has spread to the central nervous system, cancer cells can be specifically targeted by injecting drugs into the cerebrospinal fluid through lumbar puncture.
Supportive care: This entails addressing treatment-related adverse effects like exhaustion, anemia, infections, nausea, and vomiting.
Clinical Trials: Some patients might be given the chance to take part in studies looking into brand-new therapies or drug combinations for ALL.
Have you looked at : Thrombocytopenia Treatment
Diagnosis
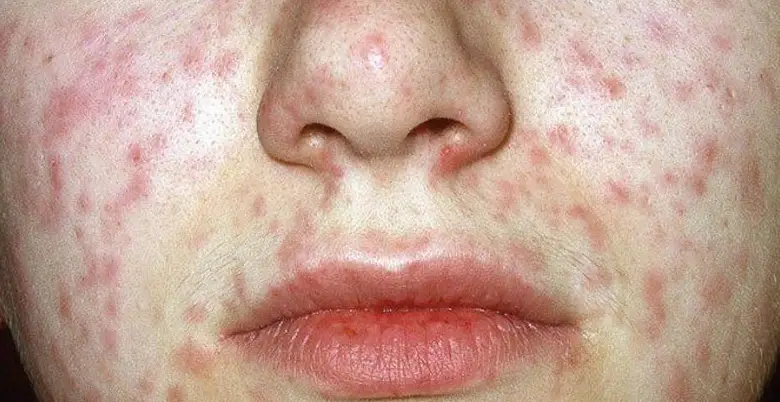
Here is an overview of the diagnostic process for ALL: Medical History and Physical Examination
Blood Tests:
A complete blood count (CBC) and specialized blood tests are conducted to assess blood cell count, including abnormalities, for leukemia, and to identify immature white blood cells.
Bone Marrow Aspiration and Biopsy:
Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy are essential for diagnosing ALL, involving aspiration of a small sample from a large bone, and examination of the resulting samples for leukemia cell analysis.
Cytogenetic and Molecular Testing:
Genetic testing and PCR can identify genetic abnormalities in leukemia cells, aiding in treatment decisions and detecting specific mutations associated with ALL.
Lumbar Puncture (Spinal Tap)
Imaging Studies
Flow Cytometry
Immunophenotypin
Outlook
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can lead to a high cure rate, particularly in children. However, delayed diagnosis can result in more advanced stages of the disease and lower chances of successful treatment.
It is crucial for healthcare professionals to promptly identify symptoms and initiate appropriate interventions to improve outcomes for patients, especially in pediatric cases.
You can also look at : Dialysis Treatment
Treatment of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia

Complications of ALL treatment may include:
- Infections
- Bleeding, anemia
- Long-term effects on organs.
Prognosis
Prognosis varies depending on factors like age, subtype of ALL, response to treatment, and genetic abnormalities.
Overall, the prognosis for ALL has improved significantly in recent years.
Risk Factors
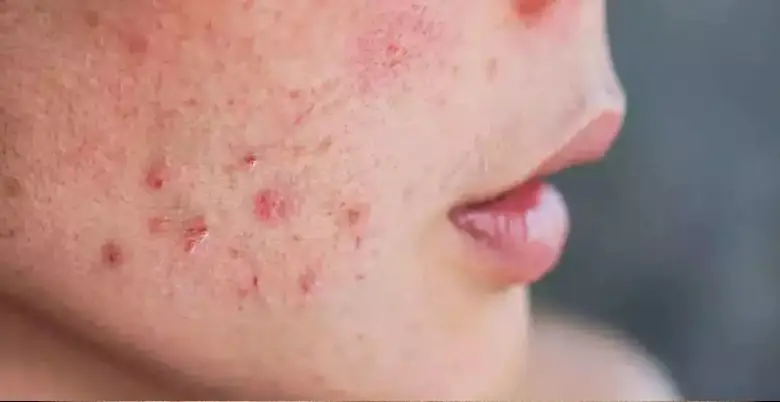
Risk factors for ALL include genetic predisposition, exposure to certain chemicals, radiation, and certain genetic syndromes.
Also read – Targeted Therapy
Side Effects
Here are some common side effects associated with ALL treatments:
- Nausea and Vomiting
- Fatigue
- Hair Loss
- Anemia
- Increased Risk of Infections
- Bleeding and Bruising
- Mouth Sores
- Changes in Appetite
- Neurological Effects
- Skin Changes
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Psychological and Emotional Effects
Pre / Post Care
- Pre-care is getting the patient ready for treatment both physically and mentally.
- Monitoring for long-term effects, dealing with difficulties, and switching to survivorship care are all part of post-care.
Explore more about –

Treatment Cost of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
- Chemotherapy: The cost of chemotherapy sessions can vary based on the drugs used and the duration of treatment. It can range from tens of thousands to several lakhs of rupees.
- Radiation Therapy: The cost of radiation therapy sessions can also vary widely. It may range from tens of thousands to lakhs of rupees.
- Stem Cell Transplant: Bone marrow transplant or stem cell transplant is a more expensive procedure. The cost can be several lakhs to a few crores (tens of millions) of rupees, depending on various factors.
- Hospitalization and Supportive Care: Hospitalization, medications, and supportive care for managing side effects and complications can add significantly to the overall cost.
- Diagnostic Tests and Imaging: Costs for tests like blood tests, bone marrow biopsies, CT scans, and other diagnostic procedures can contribute to the overall expense.