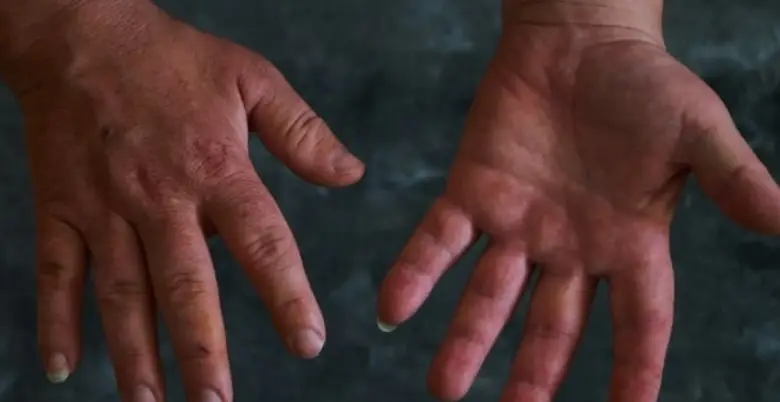
Acromegaly is a rare hormonal condition that results in abnormal bone and tissue growth by overproducing growth hormone (GH) in the pituitary gland. In order to control this illness and avoid consequences, effective treatment is crucial.
Acromegaly can cause major health issues like arthritis, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease if left untreated. Surgery to remove the tumour producing the excessive GH production, drugs to reduce GH levels, and, in certain situations, radiation therapy are all available treatments for acromegaly.
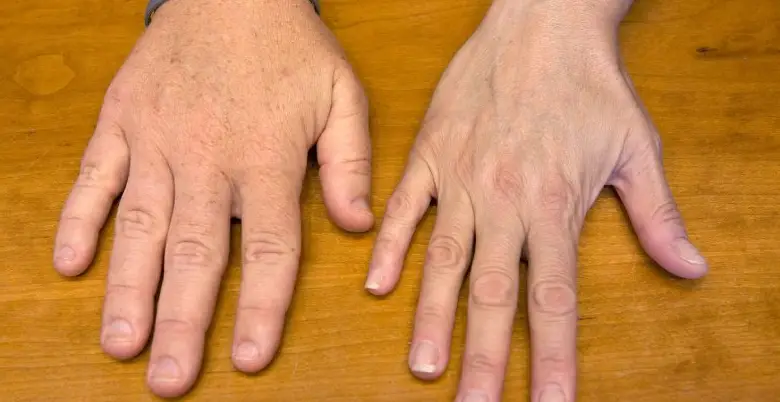
Introduction of Acromegaly
Symptoms
The symptoms of acromegaly can be subtle and may develop slowly over time. Common symptoms and physical changes associated with acromegaly include:
- Enlarged Hands and Feet
- Facial Changes
- Thickened Skin
- Deepening of the Voice
- Joint Pain
- Skeletal Changes
- Headaches
- Vision Problems
- Increased Sweating
- Fatigue
- Organ Enlargement
- Sleep Apnea
Have you looked at : Thrombocytopenia Treatment
Types
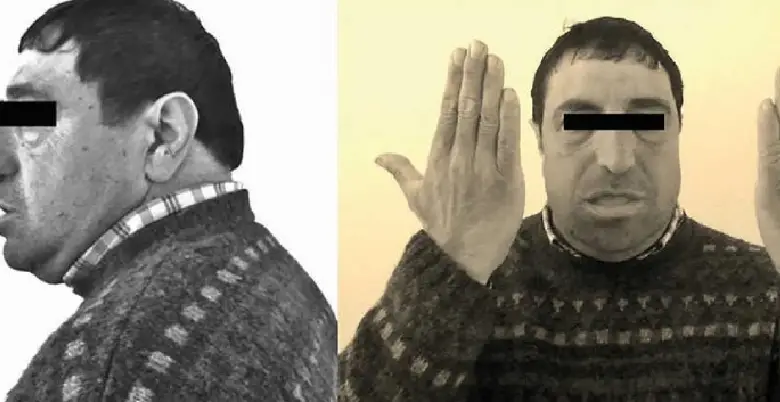

While acromegaly itself is not categorized into different types, healthcare professionals may classify it based on factors such as the cause, severity, and response to treatment.
Common classifications related to acromegaly may include:
- Sporadic Acromegaly
- Familial Acromegaly
- Secondary Acromegaly
- Invasive vs. Non-Invasive Acromegaly
- Active vs. Inactive Acromegaly
- Microadenoma vs. Macroadenoma
You can also look at : Dialysis Treatment
Diagnosis
Here are the key steps in diagnosing acromegaly:
- Clinical Evaluation:
– Medical History
– Physical Examination
– Symptom Assessment - Blood Tests:
– Growth Hormone (GH) Levels
– Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1) Levels
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
- Imaging Studies:
– Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
– Computed Tomography (CT) Scan - Visual Field Testing
- Endocrine Evaluation
- Genetic Testing
- Bone Density Measurement
Treatment of Acromegaly
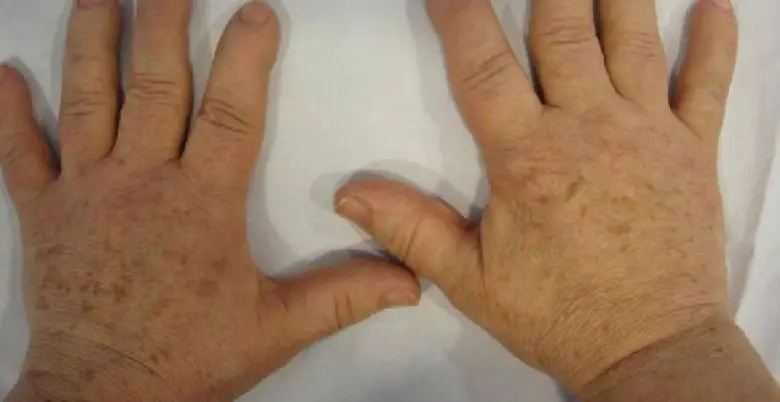
Most cases are managed with medications, such as somatostatin analogy (e.g., octreotide), which reduce GH production. Dopamine agonists and growth hormone receptor antagonists may also be used.
When medications are ineffective or not tolerated, surgical removal of the pituitary tumour (transsphenoidal surgery) may be necessary. This can be highly effective, especially for smaller tumours.
In cases where surgery and medications are not viable options, radiation therapy may be considered. This is typically used as a last resort.
Also read – Targeted Therapy
Complications
Some complications and considerations associated with acromegaly treatment include:
- Treatment Side Effects
- Surgery Complications
- Hormone Imbalances
- Tumour Recurrence
- Radiation Therapy Side Effects
- Psychosocial Impact
- Cost of Treatment
- Long-Term Management:
- Impact on Quality of Life
Prognosis

Here are some key points to consider regarding the prognosis in acromegaly treatment:
- Symptom control of acromegaly can be achieved through appropriate treatment, reducing physical changes like enlarged facial features, hands, and feet, and improving energy levels and overall well-being.
- Effective treatment aims to normalize growth hormone (GH) and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) levels in the blood.
- Proper management of acromegaly, including timely treatment and prevention of complications like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, joint issues, and sleep apnea, can significantly improve a person’s health and quality of life.
- Treatment modality, including transsphenoidal surgery, medications like somatostatin analogy, and radiation therapy, significantly impacts prognosis in pituitary tumours, potentially leading to complete cure.
- Acromegaly patients often require long-term follow-up care to monitor hormone levels, prevent tumour recurrence, and manage treatment side effects, ensuring a positive prognosis.
- Individual prognosis varies, with some individuals achieving complete remission and maintaining normal hormone levels, while others may require ongoing treatment and management for effective control.
Get information about – Aplastic Anemia
Medications (Somatostatin Analogues, Dopamine Agonists, Growth Hormone Receptor Antagonists):
– Side Effects
– Tolerance and Efficacy
– Cost
Surgery (Transsphenoidal Surgery):
– Surgical Risks
– Tumour Residual
– Hormone Deficiency
Radiation Therapy:
– Delayed Effects
– Hormone Deficiency
– Tumour Growth
Complications of Untreated Acromegaly:
– Cardiovascular Complications
– Metabolic Complications
– Joint and Skeletal Complications
– Vision Complications
– Organ Enlargement
Do read about : for your reference.
Outlook
The outlook or prognosis for individuals with acromegaly depends on several factors, including the timing of diagnosis, the effectiveness of treatment, and the management of associated complications.
You should also know – Endoscopic Spine Surgery
Side Effects

Acromegaly treatment can cause side effects like gastrointestinal disturbances, injection site reactions, gallstone formation, and liver enzyme abnormalities.
Medications like Somatostatin Analogues, Dopamine Agonists, Growth Hormone Receptor Antagonists, and Transsphenoidal Surgery can cause infection, bleeding, and damage to surrounding structures. Radiation therapy may delay hormone normalization and lead to hypopituitarism.
Pre / Post Care
The goal of preoperative care is to improve the patient’s general health. Hormone replacement treatment and hormone level monitoring may be part of postoperative care. To make sure the patient is in the best possible condition for surgery, preoperative care providers concentrate on evaluating and managing any existing medical issues, such as diabetes or hypertension. To identify any potential dangers or difficulties that might develop during the treatment, they might also do tests and screenings. In order to reduce anxiety and facilitate a quick recovery, preoperative care frequently includes teaching the patient about what to expect before, during, and after surgery.
Treatment Cost of Acromegaly

Medications: Acromegaly medications, like somatostatin analogy like octreotide, can cost between ₹10,000 and ₹50,000 per month, depending on the dosage and brand.
Transsphenoidal Surgery: The cost of transsphenoidal surgery for pituitary tumour removal can range from ₹1,00,000 to ₹5,00,000, depending on factors like hospital, surgeon fees, and post-operative care.
Radiation Therapy: The cost of radiation therapy can range from ₹2,00,000 to ₹10,00,000 or more, depending on the type of radiation and the number of sessions required.
Diagnostic Tests: Diagnostic tests like MRI, CT scans, blood tests, and hormonal assays are used in diagnosis and monitoring, costing between ₹5,000 and ₹20,000 depending on the test and location.
Hospitalization and Follow-up Care: Hospitalization costs, follow-up appointments, and ongoing monitoring should be factored in as well, which can add to the overall cost.